Ready to start your Bitcoin journey? Sign up for OKX, Binance, or Bitget today and take your first step into the world of cryptocurrency!
OKX:https://okx.com/join/8798539
Binance:https://accounts.binance.com/register?ref=1031203493
Back in 2015, the arrival of Ethereum and its smart contract functionality established the groundwork for decentralized finance (DeFi). This innovation fundamentally changed established financial systems by making transactions both trustless and open to everyone.
DeFi brought with it a variety of methods for generating income, including:
- Yield Farming: Users provide funds to DeFi platforms and earn rewards, frequently distributed in the form of extra tokens.
- Liquidity Mining: Participants contribute assets to shared pools of funds and receive tokens as an incentive, which helps to ensure the platform has enough readily available funds.
- Staking: Investors lock up their cryptocurrency holdings within a protocol to support its operations, receiving rewards as a return for their contribution.
- Restaking: Users stake their tokens across multiple platforms or levels, bolstering security and accumulating rewards from various sources.
- Liquid Staking: This allows users to stake their assets while retaining access to their value through derivative tokens, enabling them to participate in other DeFi activities.
- Decentralized Lending and Borrowing: Platforms facilitate direct lending between individuals, enabling users to gain interest by lending out their assets. Conversely, users can borrow assets by supplying collateral, gaining access to funds without traditional intermediaries.
- Fiat and Crypto-Backed Stablecoins: Stablecoins, which are linked to traditional currencies or other cryptocurrencies, offer price stability and are utilized across numerous DeFi applications.
During the initial growth of these functionalities, the Web3 landscape encountered several obstacles:
- Isolated Blockchain Networks: Blockchains functioned independently with limited exchange of value between them, hindering their ability to work together.
- Focus on Ethereum Layer 1: The majority of DeFi activity took place on Ethereum’s primary network, with other primary networks like Solana seeing adoption later.
- Complex User Experience: DeFi platforms were mainly used by enthusiasts due to their complicated interfaces and substantial transaction fees (gas fees), which prevented wider adoption.
- Limited Connection to the Real World: Beyond stablecoins, DeFi had minimal connections to tangible assets and conventional financial systems.
Since then, the crypto sphere has significantly progressed. Improvements in how blockchains communicate have led to interconnected networks with the ability to operate more abstractly. DeFi on Ethereum is shifting towards Layer 2 solutions, improving speed and decreasing transaction costs. Novel income strategies have emerged, capitalizing on these technological advancements to deliver more efficient and user-friendly financial services.
This article delves into the resurgence of DeFi, often referred to as DeFi 2.0. It explores the groundbreaking solutions that have materialized in recent years and their implications for the future of decentralized finance.
Understanding DeFi 2.0
DeFi 2.0 builds upon the groundwork of DeFi 1.0, introducing enhancements that tackle previous limitations and broaden the decentralized finance ecosystem. Let’s examine some essential characteristics that define DeFi 2.0:
Cross-Chain Ecosystem
Unlike the Ethereum-focused DeFi 1.0, DeFi 2.0 adopts a cross-chain strategy, functioning across different primary and secondary layer networks. This expansion improves how different blockchains interact and increases accessibility for users. For example, platforms like Uniswap have launched on numerous chains, including Ethereum and Polygon, to reach a larger user base.
Integration of Real-World Assets (RWAs)
Moving beyond just stablecoins, DeFi 2.0 incorporates real-world assets like bonds and property into the blockchain environment. Ondo Finance, as an illustration, provides tokenized U.S. Treasury bills, enabling users to invest in standard financial instruments through decentralized platforms.
Chain Abstraction for Improved User Experience
Chain abstraction simplifies how users interact with the system by handling complex processes behind the scenes. Users can specify what they want to do without needing to understand the underlying technical aspects like gas fees. Projects such as Particle and Omni are leading the way in implementing chain abstraction, thus enhancing the overall user experience.
Community-Driven Governance
DeFi 2.0 places emphasis on inclusive governance structures that involve the wider community, not just those holding governance tokens. This method fosters a more democratic way of making decisions, ensuring that diverse perspectives contribute to the protocol’s growth and direction.
Enhanced Liquidity Solutions
Efficient management of available funds is a defining feature of DeFi 2.0. Liquidity flows smoothly across different ecosystems, providing sufficient funds even for smaller or newer chains and projects. An example is sDAI, a synthetic asset representing DAI across multiple chains, facilitating easier transfer and use of value.
To illustrate the progression from DeFi 1.0 to DeFi 2.0, here’s a comparison table highlighting key distinctions:
| Attribute | DeFi 1.0 | DeFi 2.0 |
|---|---|---|
| Ecosystem Scope | Primarily Ethereum Layer 1 | Cross-chain, including Layer 2 solutions and various Layer 1 networks |
| Asset Integration | Limited to cryptocurrencies and stablecoins | Incorporates real-world assets like bonds and real estate |
| User Experience | Complex interfaces with high gas fees | Improved UX through chain abstraction, reducing complexity and transaction costs |
| Governance Model | Decision-making dominated by governance token holders | Community-driven governance involving a broader participant base |
| Liquidity Management | Liquidity often isolated within individual chains, leading to inefficiencies | Enhanced liquidity solutions with seamless cross-chain flow, ensuring accessibility even for niche projects |
These advancements signify a substantial step forward in the DeFi landscape, aiming to establish a more inclusive, efficient, and user-friendly decentralized financial ecosystem.
Core Innovations in DeFi 2.0
DeFi 2.0 signifies a transformative stage in decentralized finance. Expanding on the fundamentals of its predecessor, it introduces innovations that reshape how users engage with blockchain-based financial systems. These advancements are not simply technological improvements; they enable greater accessibility, efficiency, and connection with the broader Web3 ecosystem. By addressing key limitations of DeFi 1.0, such as ineffective liquidity, user experience challenges, and restricted real-world asset integration, DeFi 2.0 unlocks new possibilities for decentralized applications (DApps) and their users.
In this section, we’ll explore the pioneering projects that exemplify the core innovations of DeFi 2.0. These projects demonstrate the characteristics of this new era and highlight their significance for the evolution of Web3, paving the way for a more interconnected, scalable, and user-friendly ecosystem. Let’s delve into the innovations driving this resurgence in decentralized finance.
Improved Liquidity Mechanisms – Olympus DAO
Olympus DAO is a project focused on managing liquidity, tackling fundamental issues in DeFi related to available funds, token price stability, and building long-term value. Here’s a summary of the problems they’re addressing and their methodology:
- A Key Issue: Reliance on Short-Term Liquidity: Numerous DeFi projects depend on incentives like liquidity mining to attract initial funds. This creates “mercenary capital,” where those providing liquidity earn rewards and then remove their funds once the incentives stop, leaving protocols vulnerable.
- Over-Reliance on Centralized Stablecoins: Stablecoins such as USDT and USDC are dominant in the DeFi space, but their value is tied to centralized, fiat-backed systems. This introduces centralization risks and dependence on traditional financial institutions.
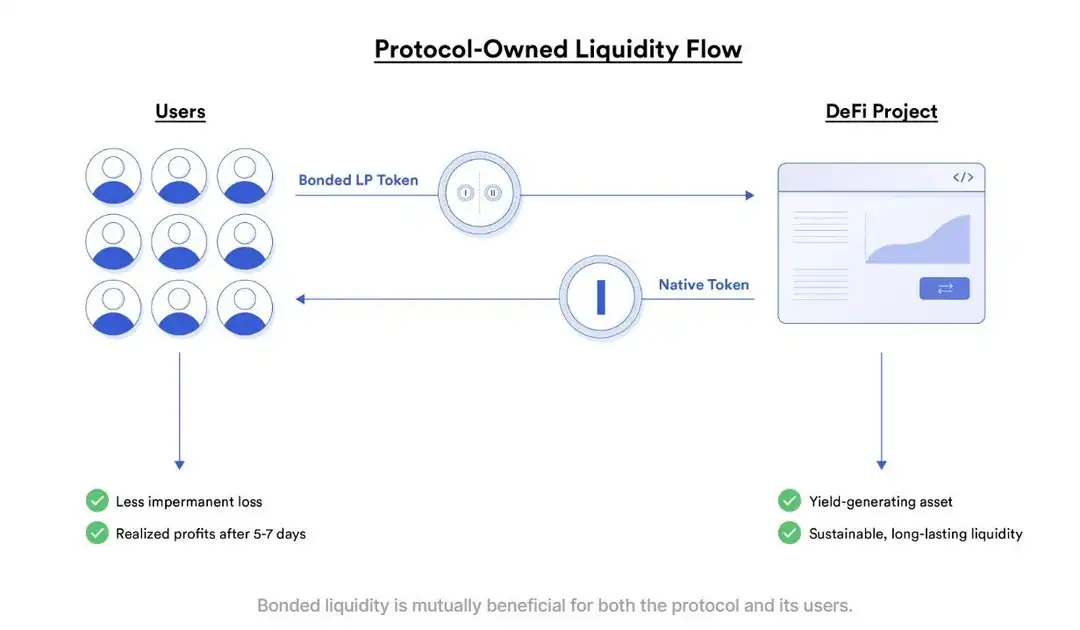
- Lack of Protocol-Owned Liquidity (POL): Most DeFi protocols don’t own the funds that ensure trading can happen smoothly and must continuously pay for this access. This is not sustainable in the long run.
- Value Accrual and Sustainability: DeFi protocols often prioritize short-term incentives and token distribution instead of developing systems for long-term value and sustainability.
How Olympus DAO is Tackling These Problems
- Introducing Protocol-Owned Liquidity (POL): The DAO utilizes a bonding mechanism to acquire its own liquidity. When a new project launches its token on a major decentralized exchange (DEX) with a prominent trading pair like ETH or USDC, users provide liquidity by locking up a pair or the token itself to receive LP tokens (representing their share of the liquidity pool).
Olympus DAO allows users to sell their LP tokens for $OHM tokens at a discounted price, effectively “bonding” the LP tokens to the protocol. This bond ensures there’s always sufficient liquidity in the trading pool, and the discount encourages users to sell their LP tokens.
- Creating a Decentralized Reserve Currency: The $OHM token, native to Olympus DAO, is a cryptocurrency-backed currency. It’s not a stablecoin but rather a reserve currency backed by a combination of crypto assets held in the Olympus treasury. The token aims to maintain its inherent value through treasury management without being tied to a specific traditional currency.
- Value-Backing Mechanism: The treasury holds assets like DAI, ETH, and LP tokens to support the value of $OHM. Each $OHM is overcollateralized, meaning the treasury holds more assets than the total circulating supply, establishing a minimum value for $OHM.
- Rebasing and Staking: Olympus DAO incentivizes long-term holding through staking. Those who stake their $OHM receive rebasing rewards, which increase their $OHM balance over time. This mechanism aligns with Olympus’s goal of creating a store of value.
- Reducing Reliance on Centralized Stablecoins: By creating $OHM as a decentralized reserve asset, Olympus aims to lessen dependence on centralized stablecoins and establish a currency native to the crypto ecosystem.
The differences between $OHM and centralized stablecoins like USDC:
| Aspect | Centralized Stablecoin (e.g., USDC) | $OHM |
|---|---|---|
| Pegged to Fiat? | Yes | No |
| Issuer | Centralized Entity (e.g., Circle) | Decentralized Protocol |
| Backing | Fiat Reserves (centralized) | Crypto Assets (diversified & decentralized) |
| Censorship Risk | High | Low |
| Value Fluctuation | Minimal | Free-Floating |
Key Takeaways
The central idea of Olympus DAO is to create a sustainable, decentralized reserve currency ($OHM) while resolving critical challenges in DeFi, such as reliance on temporary capital, over-dependence on centralized stablecoins, and a lack of Protocol-Owned Liquidity (POL). By owning its liquidity and backing $OHM with a diverse treasury, Olympus DAO is building a self-sustaining and resilient financial ecosystem that prioritizes long-term stability and decentralization over short-term incentives.
Community Driven Governance
As DeFi 2.0 emerges within the Web3 ecosystem, governance structures have evolved from centralized models to decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), empowering communities to guide project development and decision-making. This shift has introduced several key dynamics:
- Transition from Centralized Control to Community Ownership: In the early days of DeFi, project decisions were often made by a select group of promoters and initial investors. Today, DAOs distribute governance power across the community, fostering a sense of collective ownership. For instance, MakerDAO, the organization behind the DAI stablecoin, operates as a DAO where MKR token holders participate in governance decisions, ensuring that control is decentralized and community-driven.
- Empowering Users through Voting Mechanisms: DAOs enable users to directly participate in governance through on-chain voting, enhancing transparency and inclusivity. Within MakerDAO, MKR token holders can vote on crucial parameters such as stability fees and the types of collateral accepted, directly influencing the protocol’s operations. This participatory model ensures that those invested in the system have a voice in its governance.
- Increased Transparency and Accountability: On-chain voting and open proposal discussions inherent in DAOs promote transparency, as all actions are recorded on the blockchain. This record of decisions and discussions holds participants accountable and allows the community to openly audit processes. OlympusDAO, for example, utilizes on-chain governance to manage its protocol, ensuring that all governance actions are transparent and verifiable.
- Alignment of Incentives: DAOs are structured to align the interests of participants with the long-term success of the project. Many projects implement vote-escrowed tokens (veTokens), where users lock their tokens for a specific period to gain voting rights. This mechanism encourages sustained engagement and discourages short-term speculation. For instance, CurveDAO requires users to lock CRV tokens to obtain veCRV, which is essential for participating in governance and aligning voting power with long-term commitment.
- Fostering Strong Communities: DAOs incentivize active community participation through bounties, rewards, and recognition, cultivating a robust and engaged user base. By rewarding contributions, DAOs like OlympusDAO encourage members to actively participate in the project’s development and governance, strengthening the community’s cohesion and commitment.
The evolution from centralized governance to DAO-driven models in DeFi 2.0 signifies a maturation of the ecosystem, emphasizing decentralization, transparency, and community empowerment. Projects like MakerDAO and OlympusDAO exemplify these principles, showcasing the potential of DAOs to create more resilient and inclusive financial systems.
Chain Abstraction and Cross-Chain Ecosystem
Initially, decentralized finance (DeFi) was largely limited to Ethereum’s main network. Over time, the ecosystem expanded with the emergence of Layer 2 solutions and various Layer 1 blockchains like Solana, Sui, and Polygon, each developing its own DeFi environment. Currently, these ecosystems are interconnected through cross-chain technologies and chain abstraction, improving user experience and protocol efficiency.
Challenges Addressed by Chain Abstraction
Chain abstraction makes user interactions simpler across multiple blockchain networks by addressing several key challenges:
- Navigating Multiple Blockchains: Previously, users had to manually switch between different networks, each with its own interface and requirements, leading to a complex and fragmented experience.
- Fragmented Liquidity and User Base: Assets and users were scattered across various ecosystems, resulting in inefficiencies and limited access to available funds.
- Managing Multiple Wallets and Gas Tokens: Users needed separate digital wallets and native tokens to pay for transaction fees on each network, complicating asset management.
- Cross-Chain Composability: Developers faced difficulties creating decentralized applications (dApps) that could operate seamlessly across different blockchains.
- Developer Efficiency: The lack of standardized tools led to repeated efforts, hindering innovation and scalability.
Role of Chain Abstraction Projects
Projects like Omni, Across, and Particle have been crucial in implementing chain abstraction, thereby enhancing DeFi 2.0:
- Omni: Omni Network focuses on chain abstraction by providing a frontend software development kit (SDK) that applications can integrate. This allows users to interact with multiple Layer 2 solutions without needing to manually switch networks. This approach minimizes the burden of integrating with Layer 2 solutions and maintains user-friendly interactions.
- Particle: Particle Network provides solutions that abstract away the complexities of cross-chain interactions. These solutions enable users to access decentralized applications on any chain without needing to bridge assets or manage multiple gas tokens, streamlining the user experience and promoting wider adoption.
- Across: The Across Protocol facilitates efficient cross-chain value transfer, allowing users to move assets seamlessly between networks. By providing fast and cost-effective bridging solutions, Across enhances liquidity and engagement within the ecosystem.
Significance in DeFi 2.0
The incorporation of chain abstraction in DeFi 2.0 has led to:
- Simplified User Experience: Users can interact with dApps without needing to worry about the underlying blockchain complexities, encouraging greater participation.
- Unified Liquidity Pools: Assets can move freely across networks, creating more robust and accessible pools of available funds.
- Enhanced Cross-Chain Composability: Developers can build applications that are not tied to a single chain, promoting innovation and reducing redundant development work.
- Improved Developer Efficiency: Standardized tools and environments enable developers to focus on creating valuable features rather than dealing with the challenges of cross-chain integration.
By addressing these challenges, chain abstraction projects are vital in advancing DeFi 2.0, contributing to a more interconnected, efficient, and user-friendly decentralized financial ecosystem.
Integration of DeFi with the Real World
Integrating real-world assets (RWAs) into decentralized finance (DeFi) is a defining characteristic of DeFi 2.0. This approach connects traditional finance with blockchain technology to offer innovative investment opportunities.
Tokenization of Real-World Assets
Tokenization involves converting physical assets into digital tokens on a blockchain, enhancing accessibility and liquidity.
- Ondo Finance: This platform specializes in tokenizing U.S. Treasury notes, allowing investors to gain exposure to government bonds through blockchain-based tokens.
- Real Estate and Art: Platforms like Propy and Swarm facilitate the tokenization of real estate and art, enabling fractional ownership and democratizing access to high-value assets.
- Nexus Mutual: Provides coverage against risks specific to the DeFi ecosystem, such as failures in smart contracts and exchange hacks, increasing investor confidence.
- Ethena Finance Issues USDe: This platform issues USDe, a stablecoin that earns interest from staked ETH. Consequently, holders possess a stable asset that accumulates interest over time.
- Spark Protocol’s sDAI: Introduces sDAI, a tokenized representation of DAI deposited in the Dai Savings Rate (DSR). Users earn interest on their holdings while maintaining the ability to move their funds, as sDAI can be transferred, staked, or used in other DeFi applications.

These integrations represent a crucial evolution in DeFi, merging traditional financial instruments with blockchain technology to create a more inclusive and efficient financial ecosystem.
Key Takeaways
DeFi 2.0 represents a comprehensive and inclusive progression of decentralized finance. It addresses the limitations of its predecessor by introducing improved liquidity mechanisms, community-driven governance, chain abstraction, and real-world asset integration. These innovations create a more interconnected and user-friendly ecosystem, bridging the gap between traditional finance and blockchain while fostering greater accessibility and scalability. By prioritizing inclusivity, efficiency, and real-world relevance, DeFi 2.0 broadens its appeal beyond crypto enthusiasts, setting the stage for widespread adoption and a more sustainable decentralized economy.
Benefits and Risks of DeFi 2.0
Benefits:
- More Efficient Markets and Greater Liquidity: Improved liquidity mechanisms allow assets to flow freely across ecosystems, reducing inefficiencies and ensuring even niche projects have access to sufficient funds.
- Better User Experience and Greater Accessibility: Chain abstraction and simplified interfaces make DeFi 2.0 easier for users to navigate, broadening its appeal beyond tech-savvy enthusiasts.
- Real-World Solutions: Integration with real-world assets like tokenized bonds and real estate provides tangible financial solutions and expands the scope of DeFi applications.
- Lower Costs and More Variety of Products: Layer 2 solutions reduce transaction fees, while the multi-chain ecosystem offers a wider range of financial products tailored to diverse user needs.
- Varied and More Efficient Opportunities to Enhance Yield: Innovations like yield-bearing stablecoins and vote-escrowed tokens enable users to optimize returns flexibly and efficiently.
Risks:
- Real-World Products Are Untested and Operate in Regulatory Grey Areas: Tokenized real-world assets face uncertain market dynamics and regulatory scrutiny, posing legal and operational risks.
- Non-enthusiasts still Do Not Find Crypto Useful: Despite improved UX, crypto’s complexity and perceived risks may deter mainstream users who see limited value in DeFi services.
- Cross-Chain Vulnerabilities: The interconnected nature of DeFi 2.0 increases the risk of exploits and cascading failures if one network or protocol is compromised.
- Governance Challenges in DAOs: Community-driven governance can be slow, fragmented, or influenced by large token holders, potentially leading to inefficiencies or misaligned incentives.
- Liquidity Risks: While liquidity is more accessible, over-reliance on cross-chain solutions and synthetic assets can create systemic risks, especially during market downturns.
Future of DeFi 2.0
DeFi 2.0 is poised to be a transformative force in the financial world, with innovations that not only address the limitations of its predecessor but also offer unprecedented opportunities for growth. Let’s explore the potential paths forward for DeFi 2.0 and the critical developments that will shape its future.
Integration with Traditional Finance: Bridging Decentralized and Centralized Finance
One of the most promising aspects of DeFi 2.0 is its increasing connection with traditional finance (TradFi). While DeFi has already introduced innovations like tokenized real-world assets (RWAs) and decentralized lending, the future holds even more potential for bridging the divide between decentralized and centralized financial systems.
Tokenization of assets is a key area where DeFi 2.0 could enhance the traditional financial landscape. The integration of traditional assets, such as stocks, bonds, and real estate, onto the blockchain allows for wider accessibility, fractional ownership, and more efficient trading. Projects like Ondo Finance are already focused on tokenizing U.S. Treasury bonds, opening the door for retail investors to participate in government debt markets. Similarly, tokenized real estate platforms could allow individuals to invest in properties worldwide, removing barriers related to geographic location and high investment requirements.
Scaling Solutions: Role of Layer 2 Protocols in Expanding DeFi Adoption
As DeFi expands, one of its most significant challenges has been scalability. Ethereum, the primary platform for decentralized applications, has experienced issues with high transaction fees and slow processing times, particularly during periods of high usage. The emergence of Layer 2 (L2) solutions is playing a crucial role in scaling DeFi 2.0 and driving broader adoption.
Layer 2 protocols, such as Optimism, Arbitrum, and zk-rollups, offer solutions that allow DeFi platforms to operate more efficiently by processing transactions off the main Ethereum chain, significantly reducing fees and increasing transaction speeds. This improvement makes DeFi accessible to a wider audience, including users who were previously discouraged by high costs and slow processing times. As Layer 2 solutions continue to develop, we can anticipate them handling increasingly complex DeFi transactions, further expanding the ecosystem’s capacity.
Interoperability between Layer 1 and Layer 2 networks is another vital component of scaling. The future of DeFi 2.0 will involve a more interconnected ecosystem where users can seamlessly interact across multiple chains, without being concerned about high fees or fragmented liquidity. The development of projects that facilitate cross-chain communication, like Omni and Across, will make it easier for users and developers to navigate and optimize DeFi experiences, leading to greater engagement and innovation.

Evolving Use Cases: Exploring Potential Applications Beyond Financial Services
While DeFi’s primary focus has been on financial services, DeFi 2.0 is setting the stage for broader applications across various sectors. As the technology matures and becomes more user-friendly, we can expect to see decentralized solutions disrupting industries such as healthcare, supply chain management, and even gaming.
Healthcare could see significant benefits from blockchain-based solutions. For example, decentralized health records could give patients greater control over their medical data while ensuring privacy and security. Furthermore, tokenized insurance products could enable more customized, transparent, and efficient policies, driven by smart contracts and decentralized platforms.
Supply chain management stands to gain from the transparency, traceability, and efficiency that blockchain can offer. DeFi 2.0 could facilitate decentralized supply chains, ensuring real-time tracking of goods and automated contract execution without the need for intermediaries. This would reduce fraud, lower costs, and enhance the overall efficiency of global trade.
Final Thoughts: Unlocking the Future of Finance with DeFi 2.0
DeFi 2.0 represents a significant advancement in the decentralized finance ecosystem, introducing key improvements like enhanced liquidity mechanisms, community-driven governance, chain abstraction, cross-chain ecosystems, and the integration of real-world assets. These innovations address many of the challenges faced by its predecessor, making DeFi more inclusive, efficient, and accessible to a wider audience. As this space evolves rapidly, it holds immense potential to redefine financial systems and bridge the gap between traditional and decentralized economies.
If you’re intrigued by the opportunities DeFi 2.0 offers, now is the ideal time to explore projects shaping this new era. Stay informed about the latest developments to make informed decisions and capitalize on this transformative movement.
Discover how to invest in DeFi projects and gain a deeper understanding of blockchain technology with our comprehensive guides. Begin your journey into the world of decentralized finance today!
Ready to start your Bitcoin journey? Sign up for OKX, Binance, or Bitget today and take your first step into the world of cryptocurrency!